If you plan to ship goods into Canada, the Canada Border Services Agency (CSBA) will require you to submit both the Advance Commercial Information (ACI) filing and the eManifest or Electronic Manifest for security purposes. These important documents provide the organization with detailed information about your shipments prior to arrival and once they reach the border. Knowing the difference between the two can ensure efficient, fast delivery to your clients and limit your chance of having to pay costly penalties.
The ACI filing program is divided in three phases, each with their respective requirements for air, sea, rail, and truck shipments.
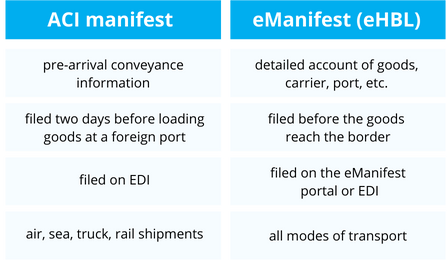
The first two phases require that air and marine carriers send pre-arrival cargo information to CBSA; the second phase is the same but for highway and rail shipments; the last phase consists in filing the eManifest shortly before the goods reach the Canadian border.
Carriers produce the ACI manifests within a given timeframe before the cargo loads at a foreign port. The eManifest, usually described as an electronic conveyance freight information, pertains to all modes of shipments and is prepared by freight forwarders and NVOCC’s on the CBSA’s eManifest portal or through Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
ACI eManifests
When filing the ACI through EDI, the following steps must be completed by carriers:
- Creating a new request and selecting their business type. They can choose between highway carrier, air carrier, marine carrier, rail carrier, warehouse operator, freight forwarders and account security holder. They must have a CBSA-issued carrier code.
- Completing their company profile.
- Authorizing an agent or any third party to interact with the CBSA on your behalf and provide the agent’s legal title and contact information.
- Authorizing a service provider or a third party to receive or share customs information with the CBSA.
- Identifying which software they will be using to provide customs information.
- Selecting the EDI messages or notices you wish to receive. Include: cargo and conveyance documents, house bills documents, supplementary documents, arrival documents or bay plan documents.
For more detailed information on ACI eManifests, go to the CBSA website.
eManifests and eHBLs
Filed by carriers, freight forwarders or NVOCCs, eManifest filed shortly before any merchandise reaches the border are referred to as eHBL, electronic house bills of lading. Essentially, they state who the carrier is, what merchandise is being carried, where it’s being delivered, and the port of crossing. Freight forwarders and NVOCCs must have an 8000-series carrier code to be able to file for a house bill of lading.
Find out more on eHBL’s in our blog article eHBL: Everything you need to know about eManifest.
Penalties
Carriers and customs brokers must comply with CBSA’s requirements when filing an ACI and eManifest. Violations can result in costly fines and may delay release of shipments. For more information on penalties and violations, consult the Administrative Monetary Penalties (AMPs) website.
Our Customs Team is Here for You
With our team of experienced customs representatives in Montreal and Toronto, we find the best solutions for your business. We know our way around customs legislation, tariffs and procedures both in Canada and abroad. Mantoria can help to process your requests, whether you are shipping small parcels monthly or high volumes of merchandise weekly.
Ask one of our agents about ACI and eManifest filing and get a quote today!
Follow our blog and our LinkedIn page for the latest updates on ACI filing and eManifests.



